Collection services terminology
Pay requests
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Payment Item | A payment item refers to an item to be paid. This can be goods or services but also bills, invoices, fines, premiums, etc.. |
| Checkout URL | A checkout URL refers to an URL that is created for each payment item. The merchant can use this link to request the debtor to pay. |
| Checkout Page | A checkout page refers to a page where the checkout URL brings the payers to select a payment method to pay with. Only when the payer attempts to pay the payment item, a transaction is created. |
| Collect Transaction | A collect transaction is an attempt to pay a certain payment item. Depending on the payment method used, it can be a card transaction or a credit transfer. |
| Payment Method | The payment method refers to the general type of payment used by a payer to complete a transaction. Examples include card payments and account-to-account payments. |
| Payment Product | A payment product refers to a specific payment solution offered to consumers and businesses for making payments. Examples: Mastercard and Visa are payment products that facilitate card payments. Note: The terms payment scheme and payment product are related but they refer to different aspects of the payment process:
|
| Payment Instrument | A payment instrument refers to an actual tool or method used to initiate and authorize a transaction. Example: in the case of Mastercard or Visa, this would be the actual card used for the payment. |
| POS | The Point of Sale (POS) is the place where a retail transaction is completed. A POS can be:
|
Recurring payments
×![]()
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
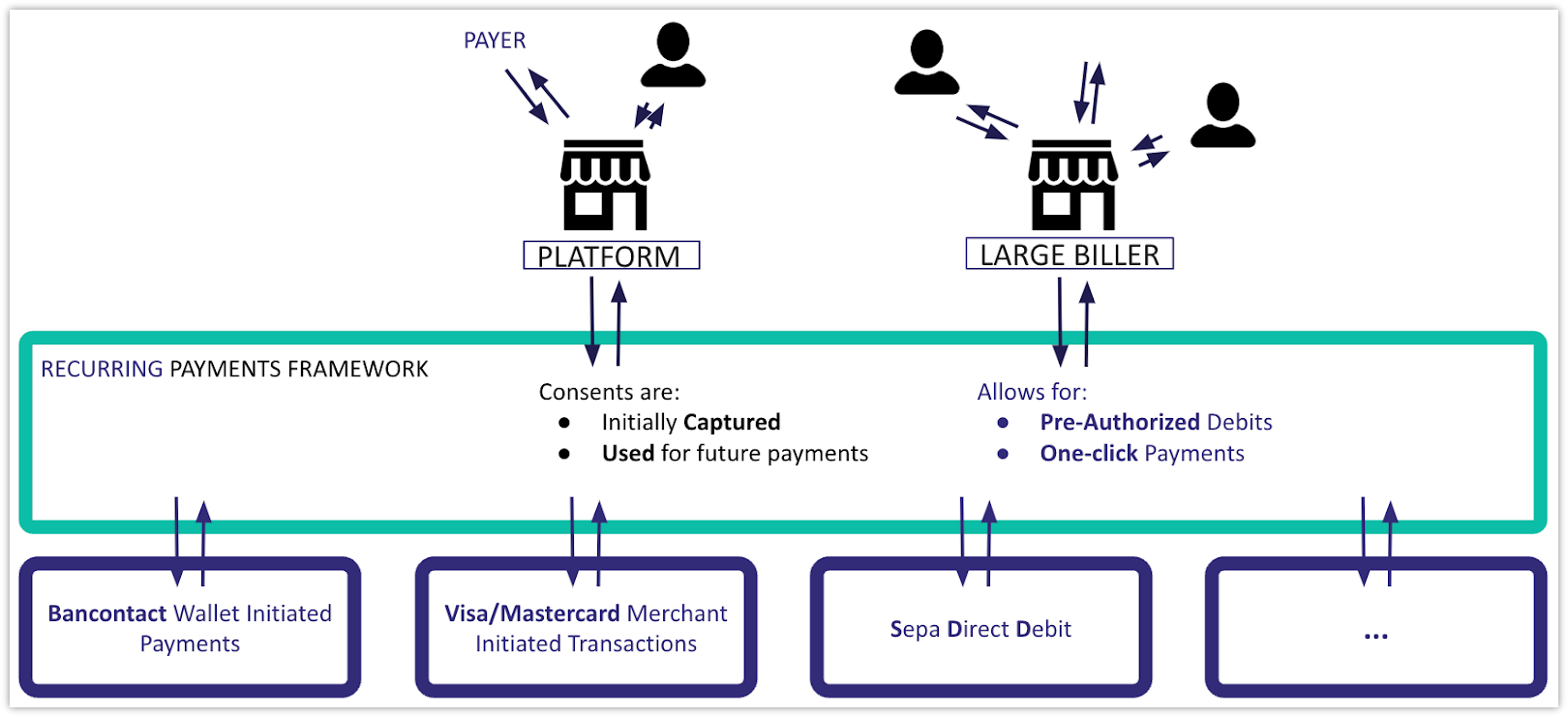
| Recurring Payments | Recurring payments refers to a payment model where the payer authorizes the merchant to pull funds from their credit card or payment account on a predefined schedule. There are two main categories of recurring payments: In theory all payment methods can support both categories, though not all use cases are equally common. For example, card payments are commonly used for both categories while SEPA Direct Debit (SDD) is usually only used for pre-authorized debits. |
| Recurring Payment Method | A recurring payment method is a payment method that can be used for recurring payments. SEPA Direct Debit (SDD) is the most well known but not the only payment method in this context. Card payments support this model as well. |
| Pre-Authorized Debit | A pre-authorized debit is a category of recurring payments where amounts (fixed or variable) are collected on a periodic basis without intervention from the payer. This is a payer-not-present payment. As it is the merchant (or the Payment Service Provider (PSP) on behalf of the merchant) who triggers the payment, it is also called a merchant initiated payment. Examples:
|
| One-Click Payment | A one-click payment is a category of recurring payments. This is a payer-present payment: the payment can be confirmed with a single click, using the previously stored payment details. Example: The buyer confirms the payment of purchases in a webshop with Mastercard without having to go through the whole authentication process. |
| Consent | A consent refers to an explicit permission from the payer to store the details of the payment instrument and (re)use it in the future to debit the account. A consent is always linked to:
|
| Consent Capture | The consent capture refers to the process of obtaining a consent. The consent can be given by the means of:
|
| Consent Item | A consent item refers to a request from the merchant to initiate a consent capture. |
| Merchant Payer Wallet | A merchant payer wallet is a place where all consents for one merchant and one payer are stored in. A wallet can contain the data of multiple payment instruments. When initiating a payment from a wallet, the system will define which payment instrument will be used. |